Introduction:
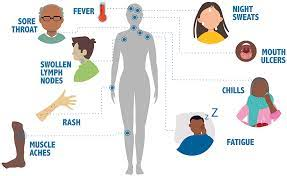
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) continue to be a significant global health concern, affecting millions of individuals each year. These infections can have serious consequences for both physical and emotional health if left untreated. In this blog post, we will explore the top 10 most common STDs, their transmission methods, symptoms, and available treatments. Understanding these infections is crucial for promoting safe sexual practices and preventing their spread.
Chlamydia:
Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most frequently reported STDs globally. Chlamydia is typically transmitted through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner.
Both men and women can contract chlamydia, and it often exhibits no noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include abnormal genital discharge, pain during urination, and pelvic pain in women. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to more severe complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, which can cause fertility issues and chronic pain.
The infection is easily treated with antibiotics, and early detection and treatment are essential to prevent further complications and halt the transmission of the infection.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV):
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, weakening its ability to fight off infections and diseases. HIV is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing contaminated needles, and from an infected mother to her child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
Once inside the body, HIV targets CD4 cells, a type of white blood cell crucial for immune function. As the virus replicates and destroys these cells, the immune system becomes progressively compromised, leading to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) if left untreated. HIV can remain asymptomatic for years, making early detection through testing vital to manage the infection effectively.
With advances in medical treatment, antiretroviral therapy (ART) has transformed HIV from a life-threatening condition to a manageable chronic illness. ART helps suppress the virus, allowing individuals with HIV to lead healthier lives and significantly reducing the risk of transmission to others. However, there is still no cure for HIV, making prevention and education crucial in curbing its spread.
Gonorrhea:
Gonorrhea is another bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Like chlamydia, it is transmitted through unprotected sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Gonorrhea can affect the genitals, rectum, and throat, and symptoms may include painful urination, abnormal genital discharge, and swollen testicles in men. However, similar to chlamydia, many infected individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms.
If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to severe health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and epididymitis (inflammation of the tubes carrying sperm) in men. Additionally, untreated gonorrhea increases the risk of HIV transmission.
Gonorrhea is treatable with antibiotics, but antibiotic-resistant strains have emerged in recent years, making regular testing and early treatment critical in preventing its spread and managing the infection effectively.
Syphilis:
Syphilis is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It progresses through stages, and each stage presents different symptoms and complications.
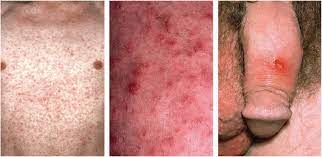
The primary stage of syphilis is characterized by the appearance of a painless sore, known as a chancre, at the site of infection, usually the genitals, anus, or mouth. The secondary stage involves a rash that can affect the palms and soles, as well as flu-like symptoms.
If left untreated, syphilis can progress to the latent and tertiary stages, where the infection can cause severe damage to the organs, including the heart and brain.
Syphilis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact but can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy or childbirth.
Penicillin is the standard treatment for syphilis, and early detection and treatment are crucial to preventing long-term complications and halting the transmission of the infection.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV):
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of viruses that can cause various infections in both men and women. It is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections globally.
There are more than 100 types of HPV, and while some strains cause genital warts, others are linked to the development of cervical, anal, penile, and other types of cancers.
HPV is primarily transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The virus can also spread through non-sexual means, such as from mother to child during childbirth.
Many people infected with HPV may not exhibit symptoms, making regular screening, including Pap smears and HPV tests, essential for early detection of cervical abnormalities and prevention of cervical cancer.
There is no cure for HPV, but most infections clear on their own without causing harm. Vaccines are available to protect against certain high-risk HPV strains and are recommended for both males and females to reduce the risk of developing HPV-related cancers and genital warts.
Herpes (HSV):
Herpes, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), is a common viral infection that manifests as oral herpes (cold sores) or genital herpes. There are two types of HSV: HSV-1, which primarily causes oral herpes, and HSV-2, which is responsible for most cases of genital herpes.
Herpes is transmitted through direct contact with a herpes sore during sexual activity, including kissing and genital-to-genital contact. The virus can also spread through contact with infected saliva or genital secretions, even in the absence of visible sores.
Many individuals infected with herpes may not experience symptoms or may have mild symptoms, making it challenging to detect and prevent transmission.
While there is no cure for herpes, antiviral medications can help manage and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Safe sexual practices, including the use of condoms and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks, can reduce the risk of transmission to partners.
Trichomoniasis:
Trichomoniasis is a common parasitic infection caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. It affects both men and women but is more commonly symptomatic in women.
Trichomoniasis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact with an infected partner, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Common symptoms of trichomoniasis in women include vaginal itching, burning during urination, and abnormal vaginal discharge with a strong odor. Men may experience itching or irritation inside the penis or mild discharge from the penis.
Trichomoniasis is treated with prescription antibiotics, and both partners should receive treatment simultaneously to prevent reinfection.
Hepatitis B and C:
Hepatitis B and C are viral infections that primarily affect the liver. They can be transmitted through sexual contact with an infected partner, sharing contaminated needles, or from an infected mother to her child during childbirth.
Hepatitis B and C can cause both acute and chronic infections. Chronic infections can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and other serious health complications.
Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination, and there are effective antiviral treatments available to manage chronic hepatitis B and C infections.
Bacterial Vaginosis:
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection caused by an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina. It is not considered a sexually transmitted infection, but sexual activity can impact the balance of vaginal bacteria and increase the risk of BV.
BV is characterized by symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge with a fishy odor, itching, and irritation.
Treatment for BV typically involves prescription antibiotics, and avoiding douching and using scented products in the genital area can help prevent recurrent infections.
Pubic Lice (Crabs):
Pubic lice, also known as crabs, are parasitic insects that infest the coarse hair of the genital area. They can also be found in other body hair, such as in the armpits, chest, and beard.
Pubic lice are transmitted through close physical contact with an infected person or through sharing contaminated bedding or clothing.
Symptoms of pubic lice infestation include itching and the presence of lice or their eggs (nits) attached to the hair.
Treatment for pubic lice involves using medicated shampoos or lotions that kill the lice and their eggs. Additionally, thorough cleaning of bedding and clothing is necessary to prevent re-infestation.
It is important to remember that prevention, regular testing, and safe sexual practices are essential in reducing the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases. Seeking medical advice and treatment promptly can help manage and prevent potential complications associated with these infections.
Conclusion:
Understanding the top 10 common sexually transmitted diseases is crucial for promoting sexual health and preventing their spread. Regular testing, safe sexual practices, and open communication with partners are essential in reducing the transmission of these infections and ensuring a healthier and safer future for everyone. Seeking medical advice and treatment promptly can help manage and prevent potential complications associated with these infections. Remember, prioritizing sexual health and well-being is key to leading a fulfilling and healthy life.